Since 2006, the Institute of Geodynamics in cooperation with the Acropolis Restoration Service (YSMA) has deployed an accelerometric array of 10 instruments. The complex geological conditions, the topography and the human earthwork interventions (filling materials) affect the modulation of ground motion. This instrumental seismic monitoring within the area of the Athens Acropolis records the effects of earthquakes on the monuments and results in extracting useful information concerning their response and furthermore the dynamic properties of materials.
NOAGI and the Acropolis Restoration Service (YSMA) are in cooperation for the study of strong ground motion on the Acropolis hill since 2006. Within this frame, a digital 12bit accelerograph was first installed and connected via SYZEFXIS network for telemetric maintenance and data retrieval. Since the Acropolis hill is exposed to extreme weather conditions (snow, heavy rain, low or high temperatures) special care was taken for the reliable operation of the instrument.
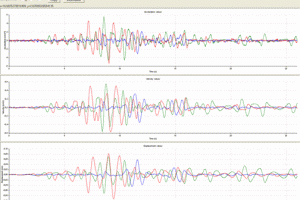
This accelerograph recorded two long distance earthquakes, namely that of Andravida (8/6/2008, M=6.5, R=195km, PGA=0.006g) and that of Mantoudi (14/10/2008, M=5.6, R=100km, PGA=0.004g), which are the first ever recordings at the Acropolis archaeological site.
Since 2008, NOAIG has undertaken a project to upgrade and extend towards a strong motion array, which today consists of 10 modern 24-bit instruments (CMG-5TDE type) in operation.
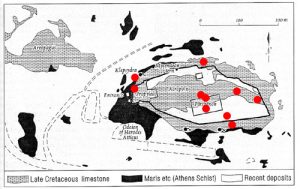
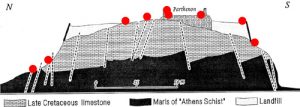
The accelerographs were installed on small, specifically constructed vaults, at sites that were selected with criteria to cover the broader hill, the monuments under investigation and the ground classification.
|
CODE |
REMARKS |
| ACRA | Limestone |
| ACRB | Parthenon floor, north colonade |
| ACRC | Parthenon cornice, north colonade |
| ACRD | Southern wall, fillmaterials |
| ACRE | Eastern wall,limestone |
| ACRF | Northern wall, foot, limestone |
| ACRG | Athenian schist(bedrock) |
| ACRH | Propylaia, Limestone |
| ACRI | Parthenon floor, south colonade |
| ACRJ | South wall, foot, limestone |
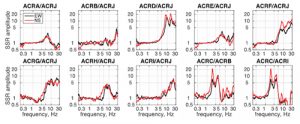
Currently, a database has been developed including more than 700 3-component records representing about 70 earthquakes of various magnitudes and epicentral distances.Although records of near-field moderate earthquakes do not exist so far, as events have not occurred during this recording period, processing of the recorded accelerograms demonstrate the strong effect of the geotechnical properties at the recording installation sites.
Selected Relevant References:
- Ambraseys, N. (1985). On the protection of historical monuments and sites in seismic areas. Proc. 2nd intern. Conf. for the protection of Parthenon, Athens, vol1, 207-228.
- Andronopoulos, B. and Koukis, G. (1990). Engineering proplems in the Acropolis of Athens. Engineering Geology of Ancient Works, Monuments and Historical Sites, P. Marinos and G. Koukis (editors), Balkema, Rotterdam, 1819-1831.
- Egglezos, D. (2010). Exploitation of contemporary technological applications for the preservation of the Acropolis Circuit Wall. Acropolis Restoration News, issue 10.
- Egglezos, D., Ioannidou, M., Moullou, D. and Kalogeras, I.(2013). Geotechnical issues of the Athenian Acropolis. in Carlo Viggiani (edit.), Geotechnics and Heritage, Case Histories, CRC Press, 13–47.
- Cauzzi, C., Kalogeras, I., Melis, N., Stupazzini, M., Mazzieri, M. and Clinton, J. (2015). Preliminary Results on the Seismic Response of the Acropolis of Athens (Greece) through Recorded Earthquake Data and Numerical Simulations. 6th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering, 1-4 November, Christchurch, New Zealand.
- Higgins, M. and Higgins, R. (1996). A geological companion to Greece and the Aegean. Gerald Duckworth & Co Ltd., 29-30.
- Kalogeras, I. and Egglezos, D., 2013. Strong motion record processing for the Athenean Acropolis seismic response assessment. Proceedings of Geotechnical Engineering for the Preservation of Monuments and Historic Sites, Napoli, Italy 30-31 May.
- Kalogeras, I., Evangelidis, C., Melis, N. & Boukouras, K., 2012. The Athens Acropolis Strong Motion Array. EGU General Assembly. Geophysical Research Abstracts, vol. 12. EGU 1012-9523, Vienna, Austria.
- Kalogeras, I., Stavrakakis, G., Melis, N., Loukatos, D. and Boukouras, K. (2010). Deployment of the strong motion array at Athens Acropolis area: Implementation and prospects. Acropolis Restoration News, issue 10.
- Sakellariou, M., Kalogeras, I., Kapogianni, E., and Psaropoulos, P. (2016). Investigation of the dynamic behaviour of the Periphera Acropolis Wall against seismic loading by using combined instrumental monitoring of optical fibre sensors and accelerographs. Final technical report, submitted to John Latsis’ Public Benefit Foundation, 55pp (in greek).
- Stavrakakis, G.N. (2009). Earthquake Hazard Assessment for the Athens Acropolis area. National Observatory of Athens, Report submitted to Acropolis Restoration Service, 47pp (in Greek).